Contents
5. Calculations
![]() Updated
by Mapidea Team
Updated
by Mapidea Team
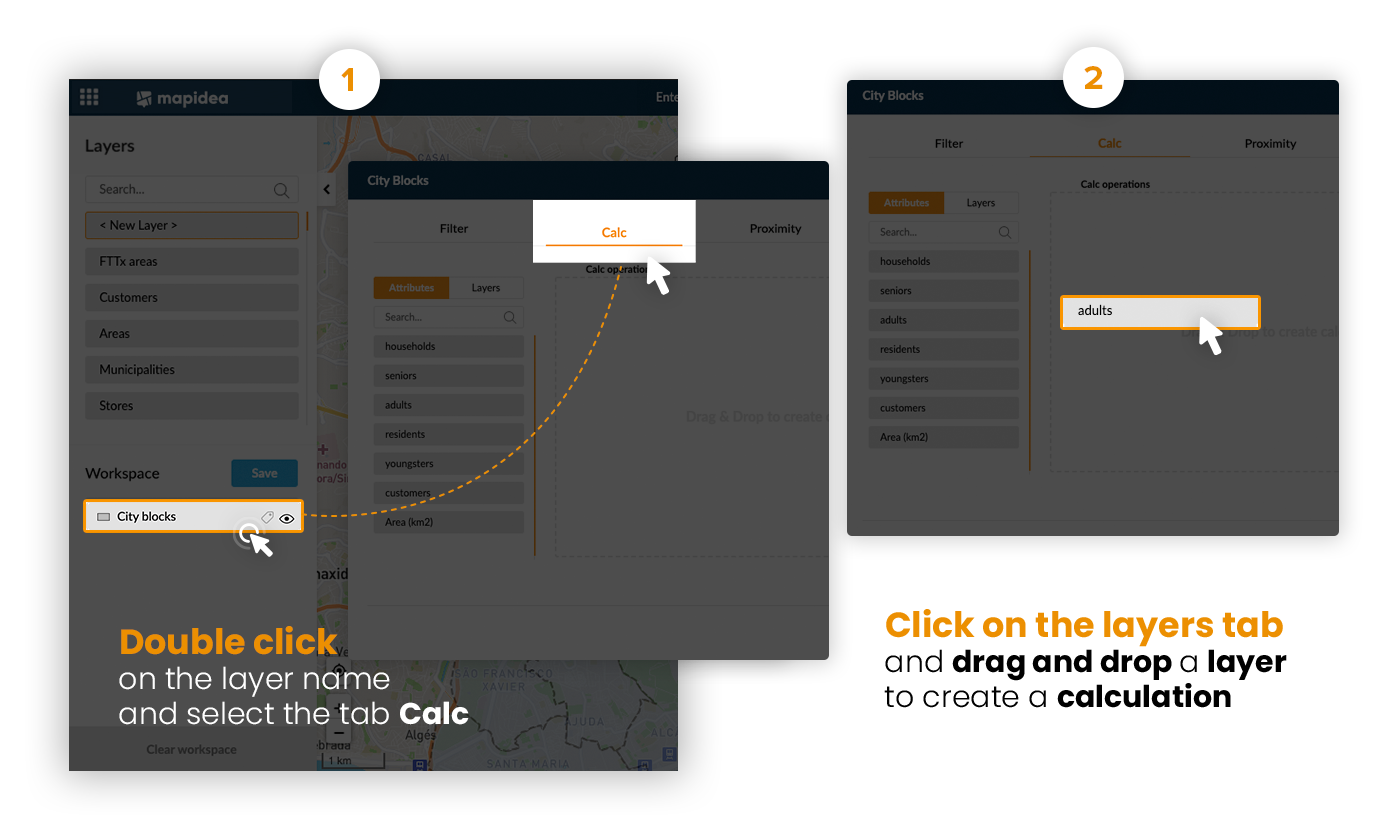
Calculations is one of the most powerful feature available in Mapidea. It allows the users to create new data based on arithmetic operations or geographic relations.
5.1 Arithmetic calculations
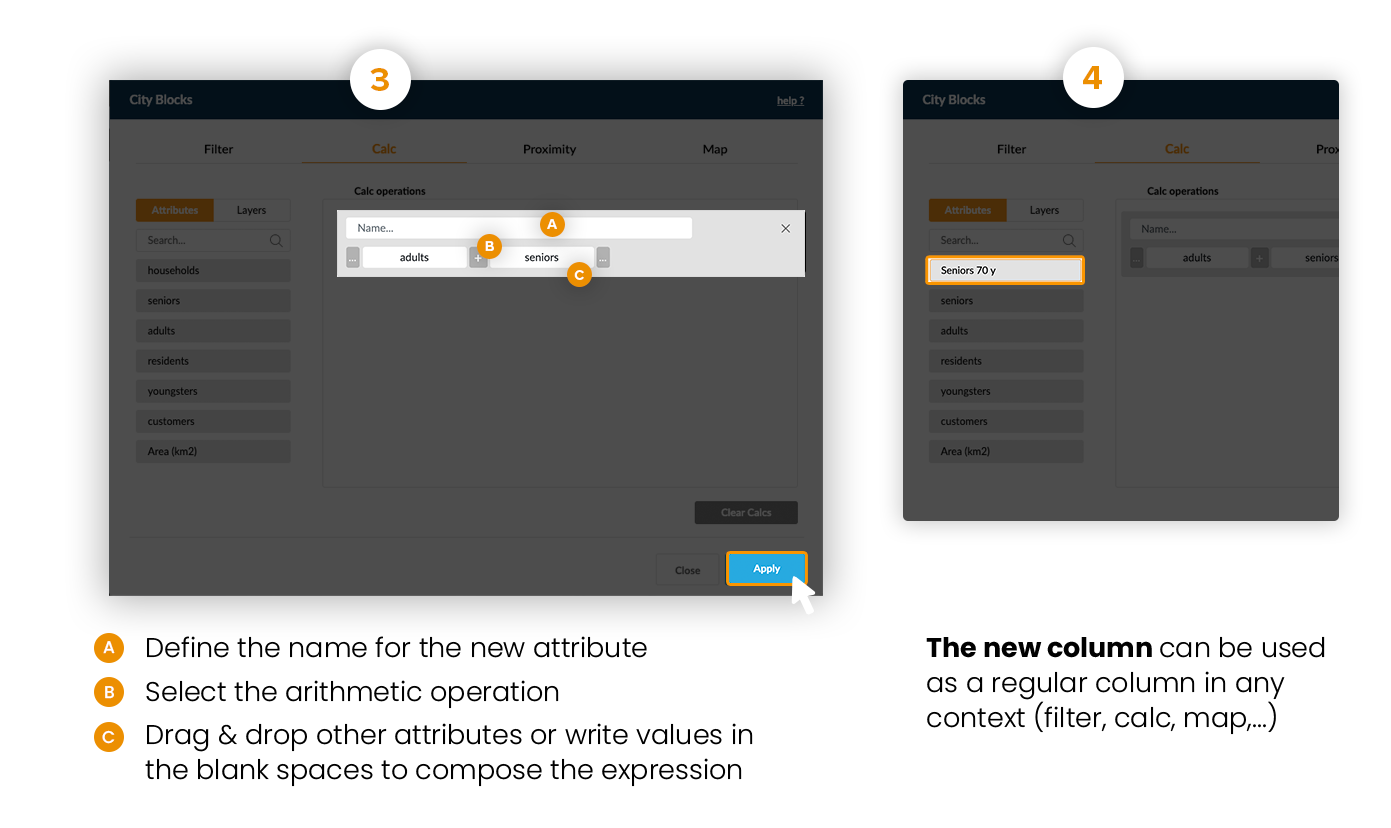
It's possible to create new columns with data resulting from arithmetic calculations - from the attributes available in the attributes list.
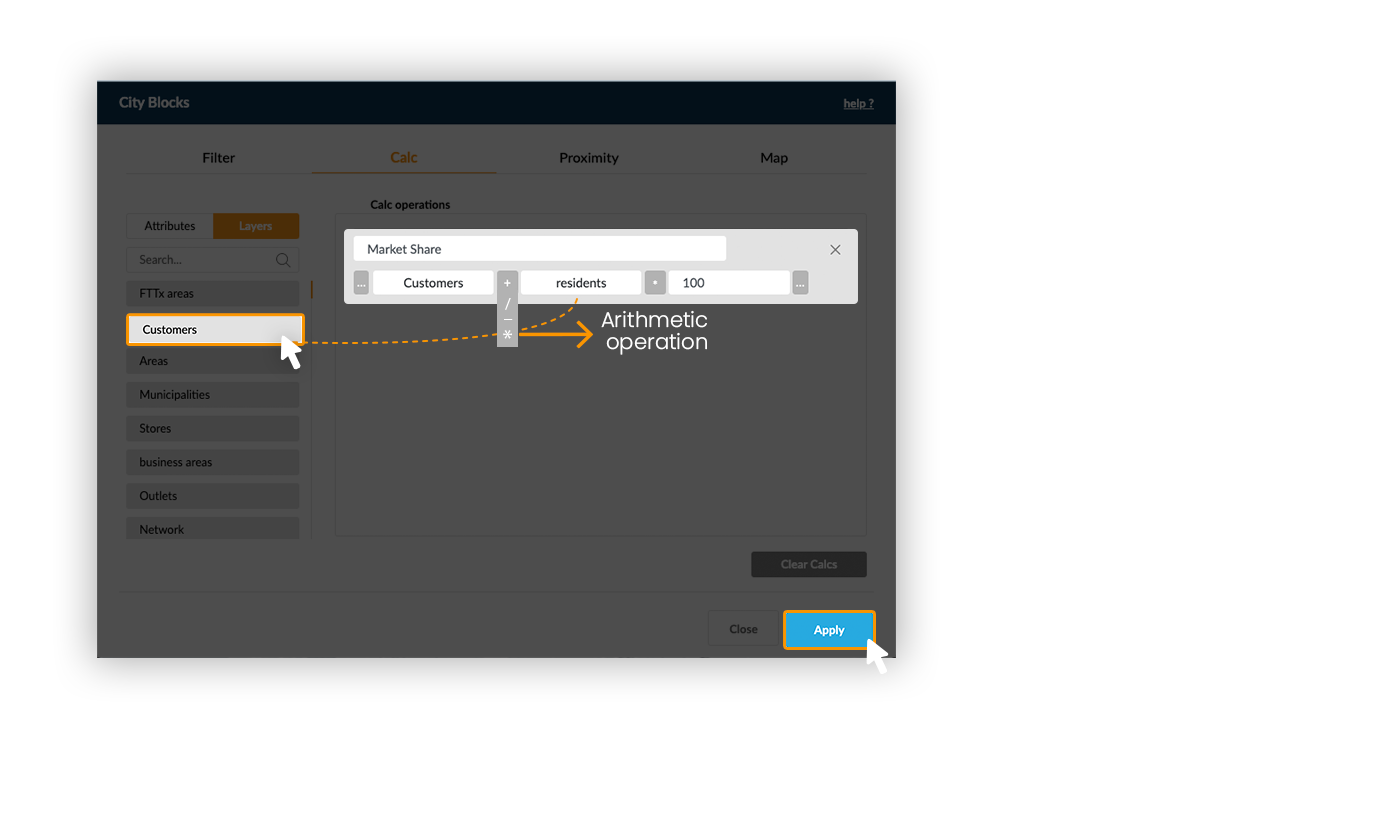
Example: Calculate the market share by region, by dividing the number of customers per the number or residents and multiplying by 100.

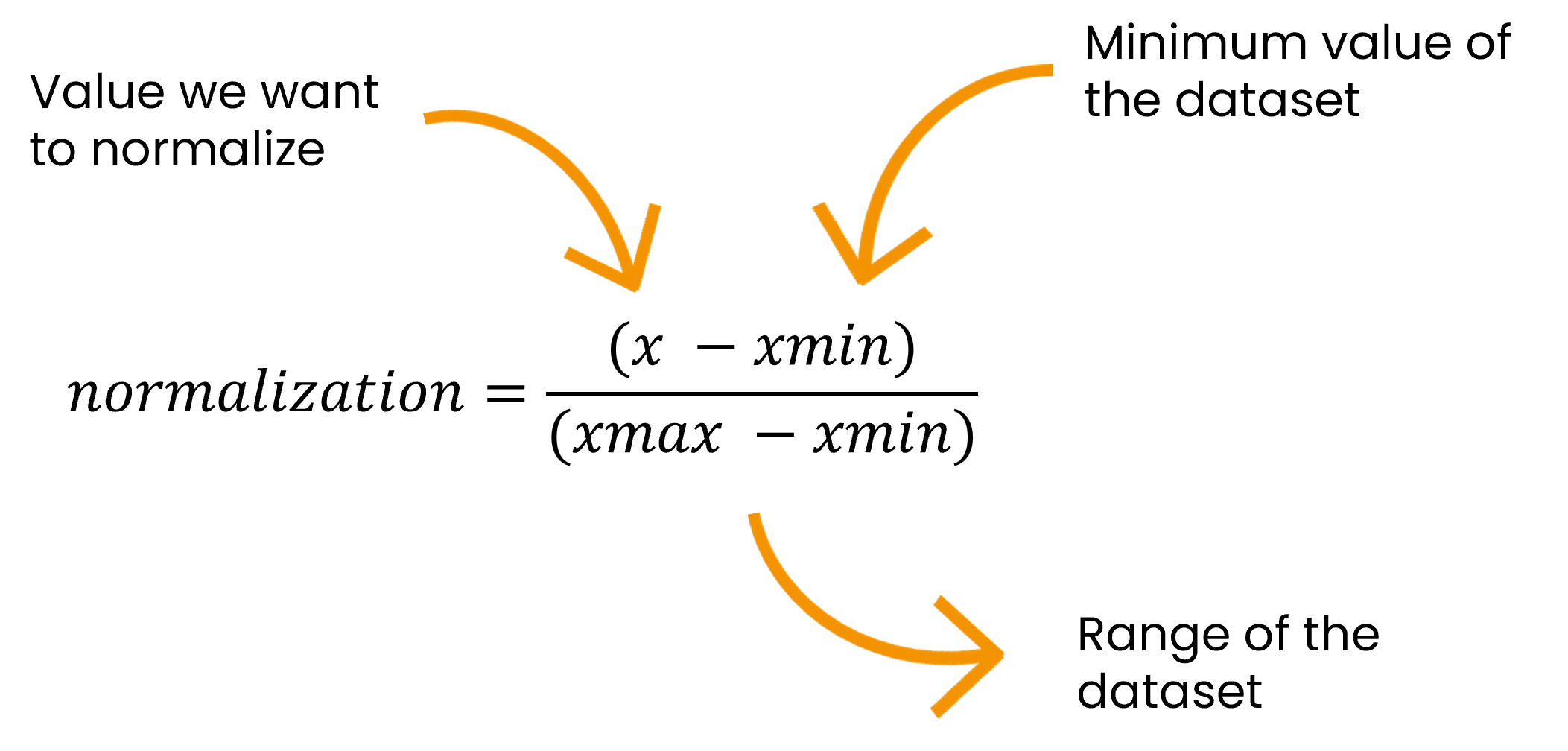
5.1.1 Normalize attributes
Normalization is a mathematical formula that removes units of measurement from data, allowing you to compare data from different sources. It can be useful for anyone who is interpreting data, and great for creating models with datasets with different measures.
See the formula and an example below.
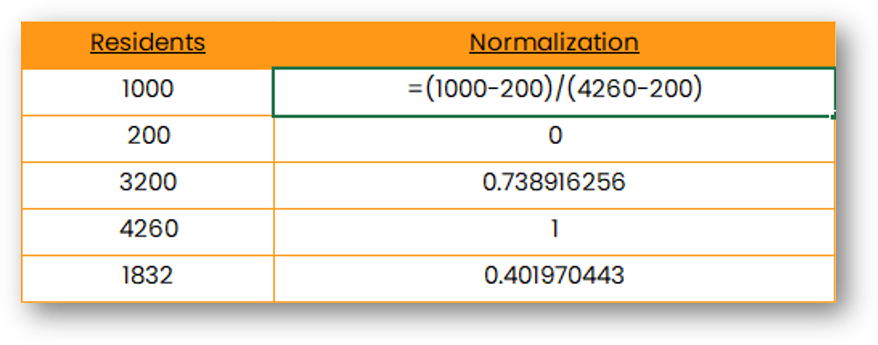
Now, when doing arithmetic calculations a new option will appear next to the parenthesis.
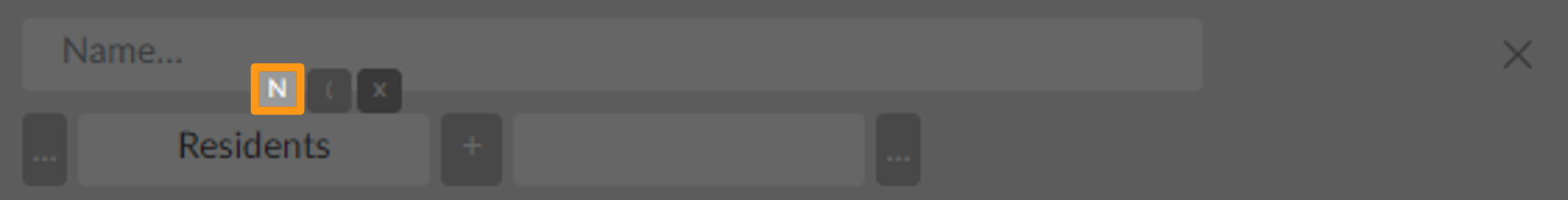
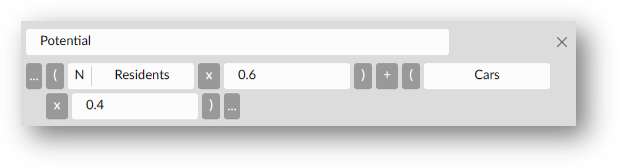
To normalize a layer, just click on the "N" button. If you want to make a calculation with more than an attribute normalized, you can just keep going with arithmetic calculation (example below).
5.2 Geographic calculations
It's possible to create new columns based on a geographic relation between different layers. Press layers to access the layers list (switch from the attributes list).
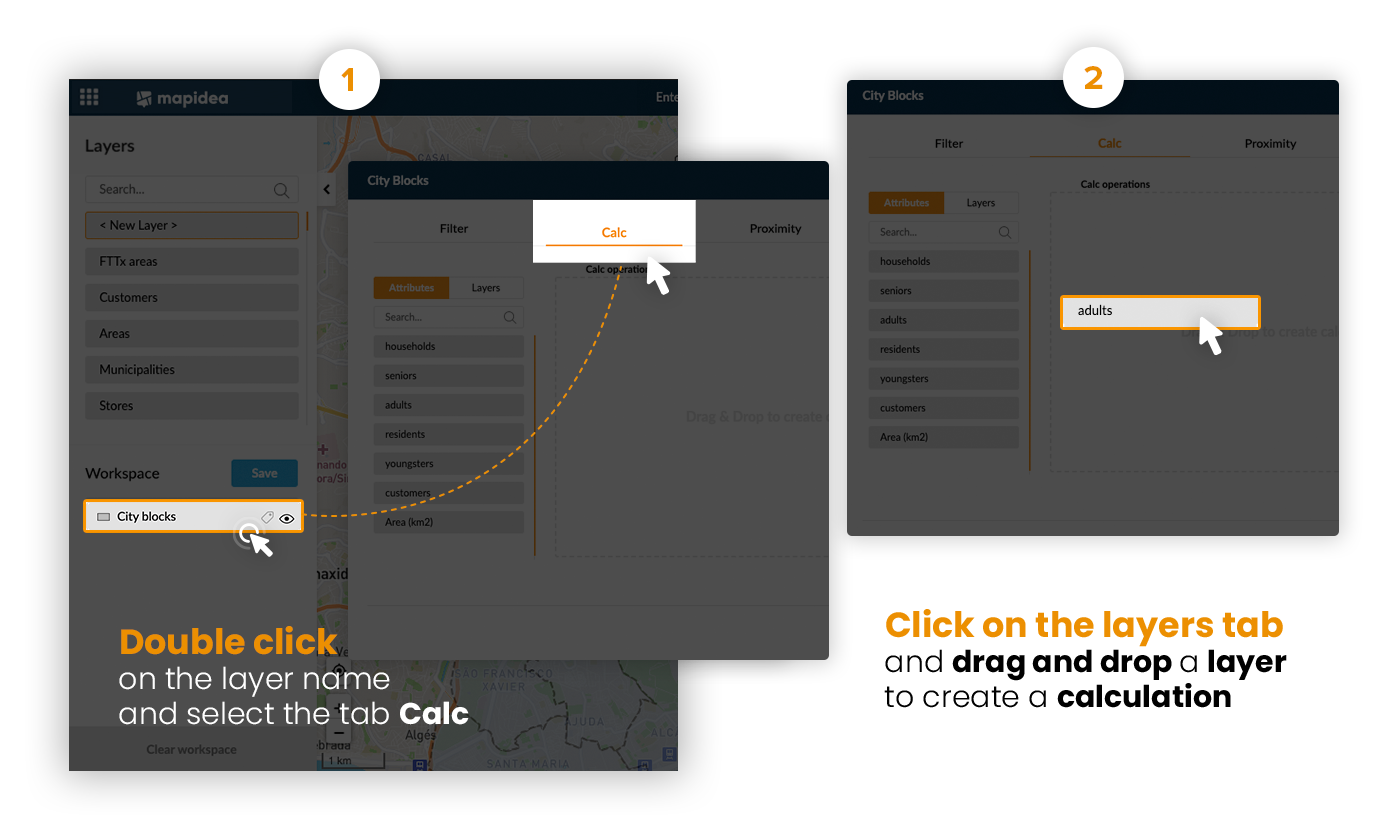
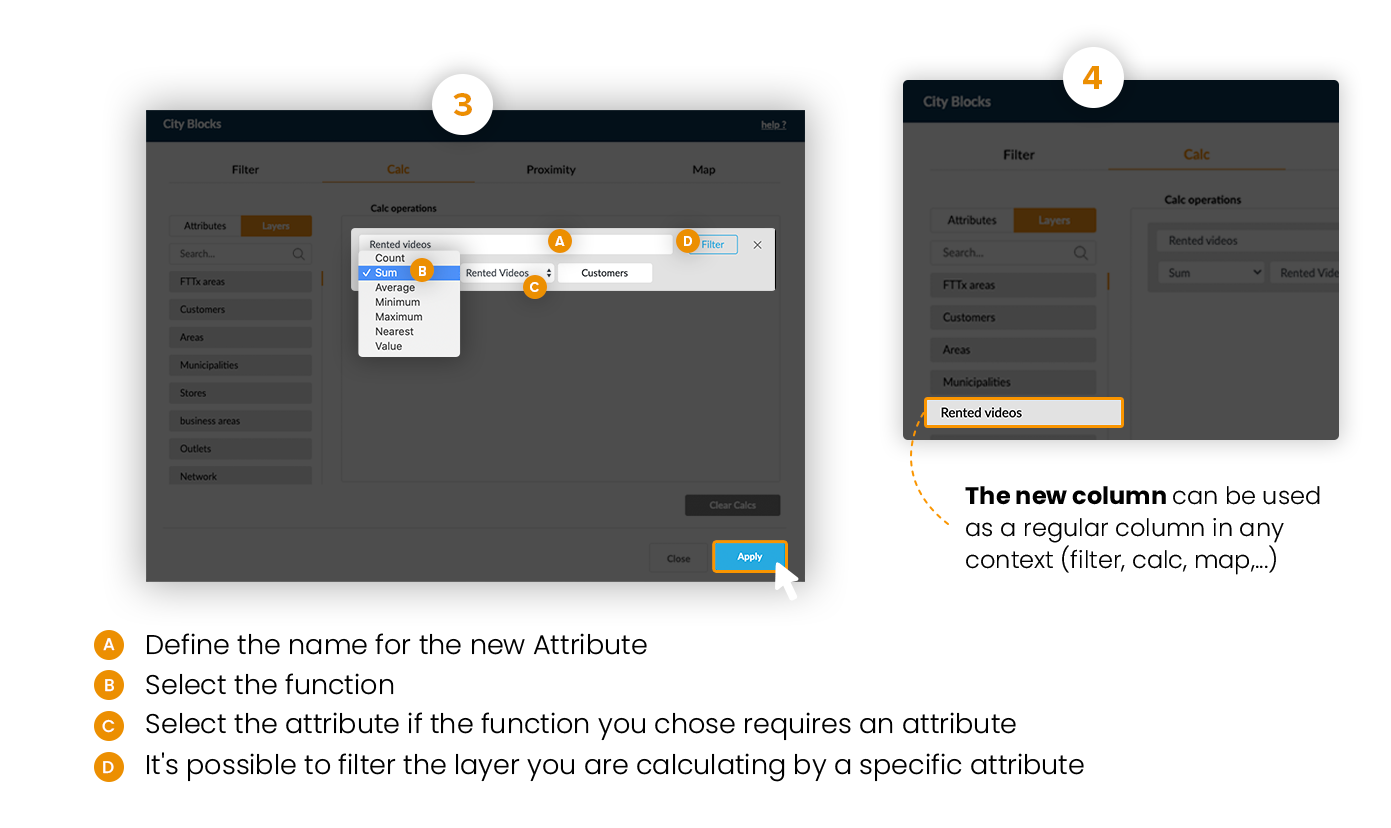
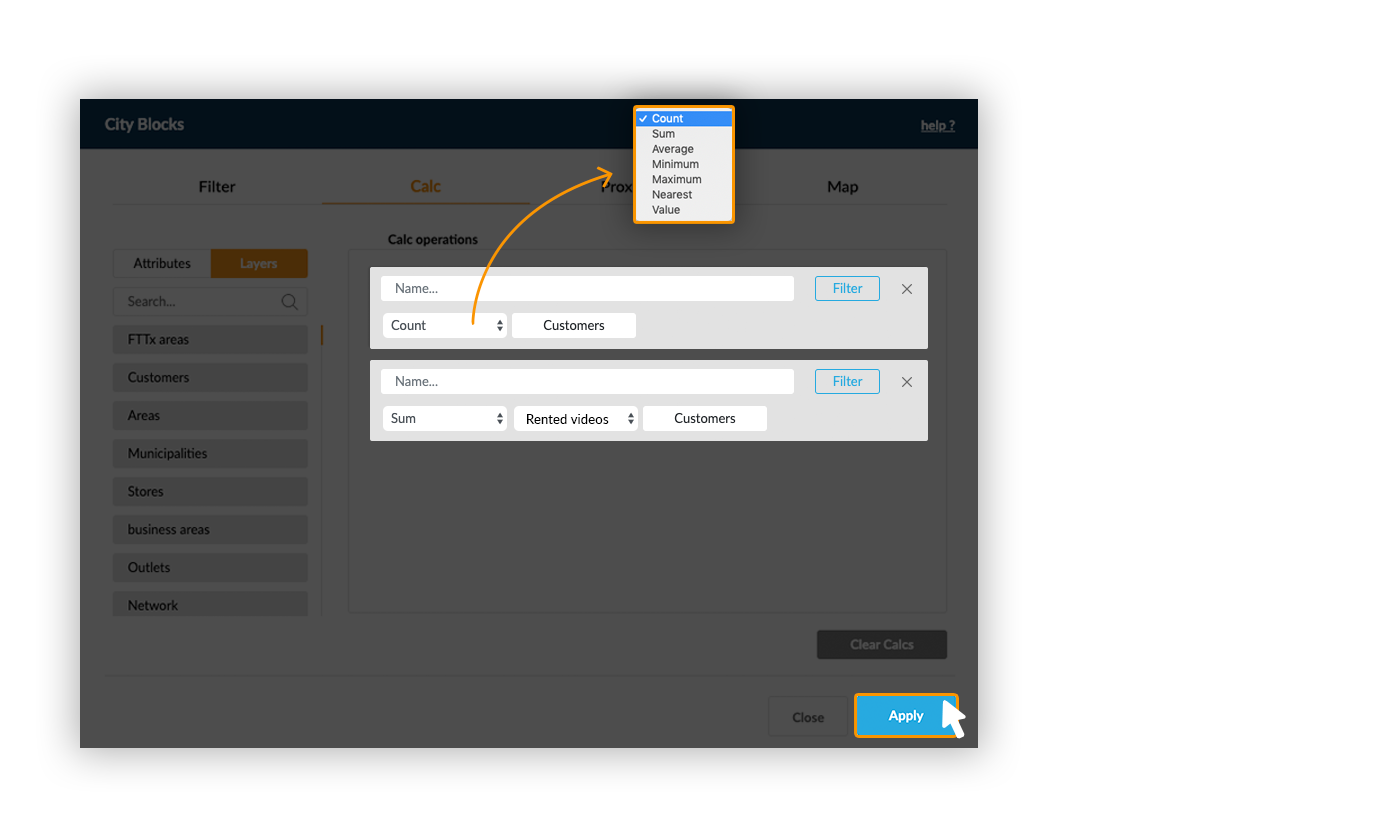
Example: Count the number of customers and sum their rented videos within business areas.
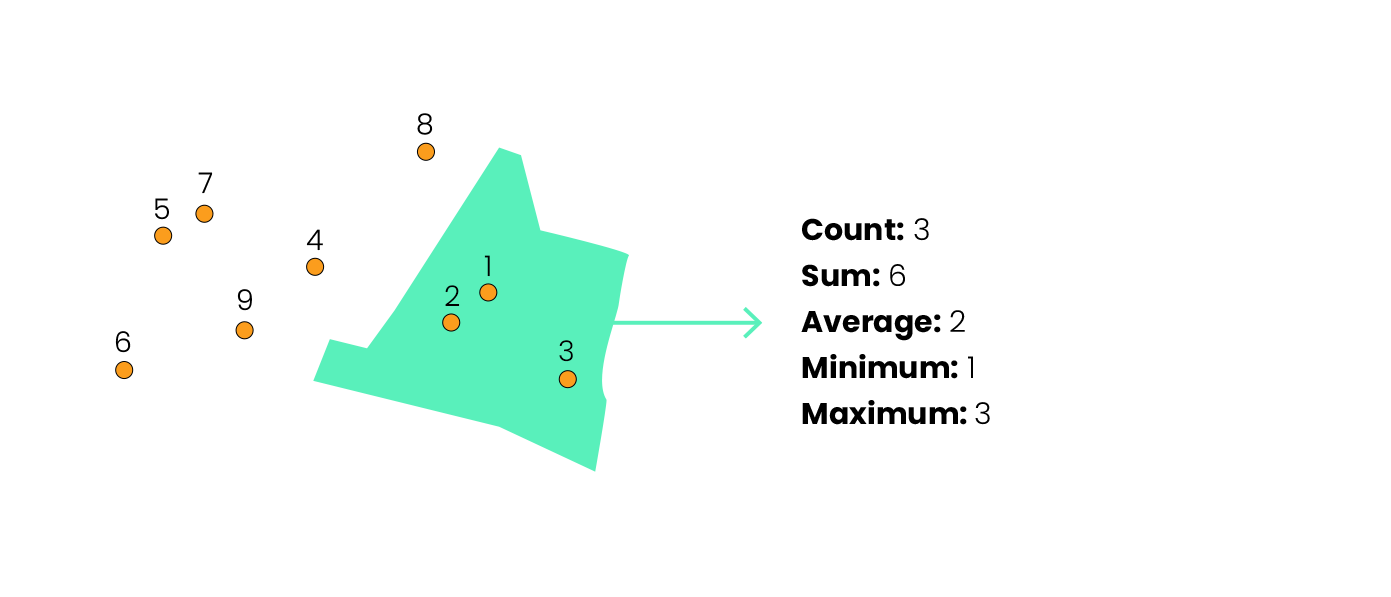
The Count operator doesn't need any additional parameters: it counts the number of elements from the used layer within each element of the target layer.
When using a statistical function (Sum, Avg, Min and Max), it’s necessary to indicate which attribute should be used.
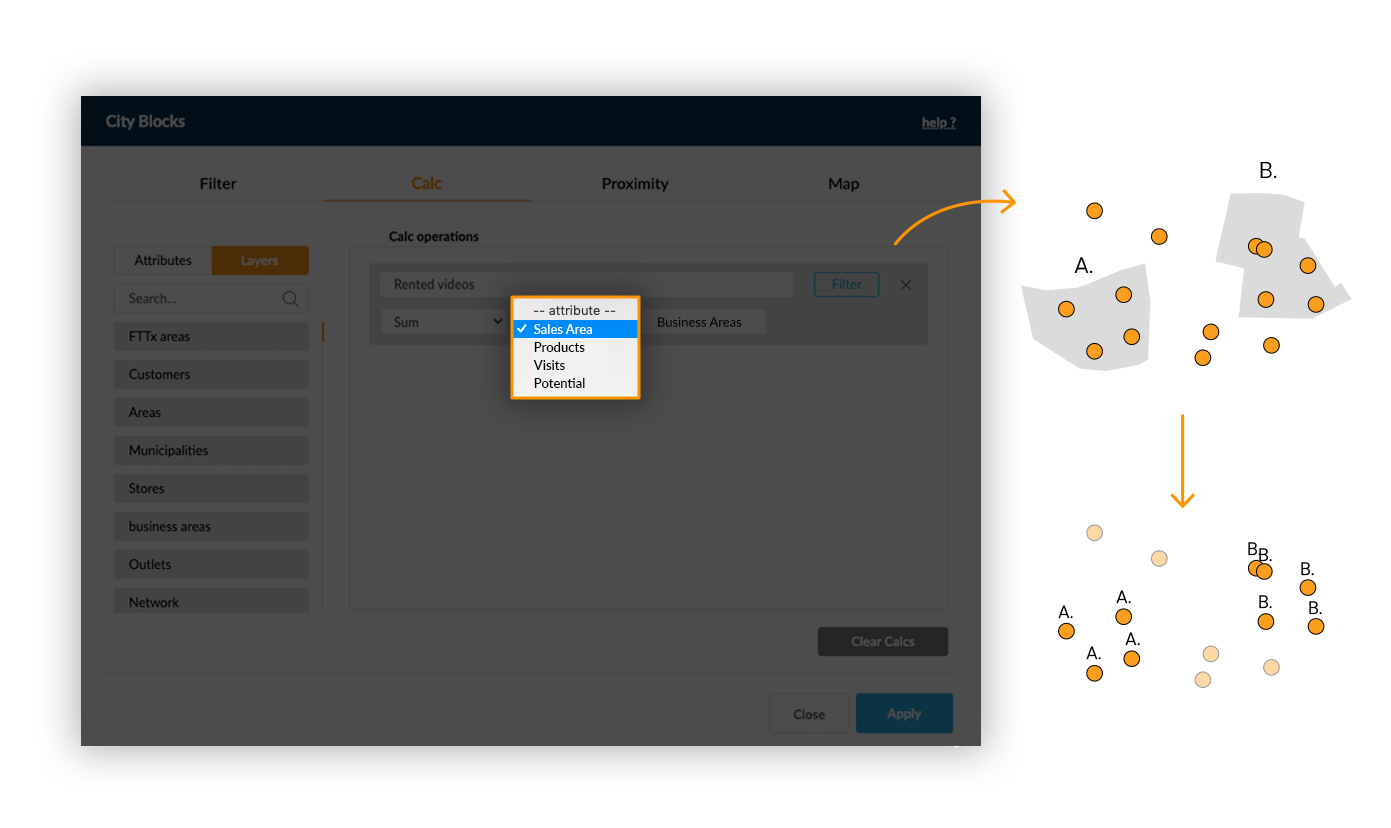
When using the Value function, values from one layer are directly transposed to the target layer by a contains spatial relation.
Example: Add the area code for each element from a point layer:
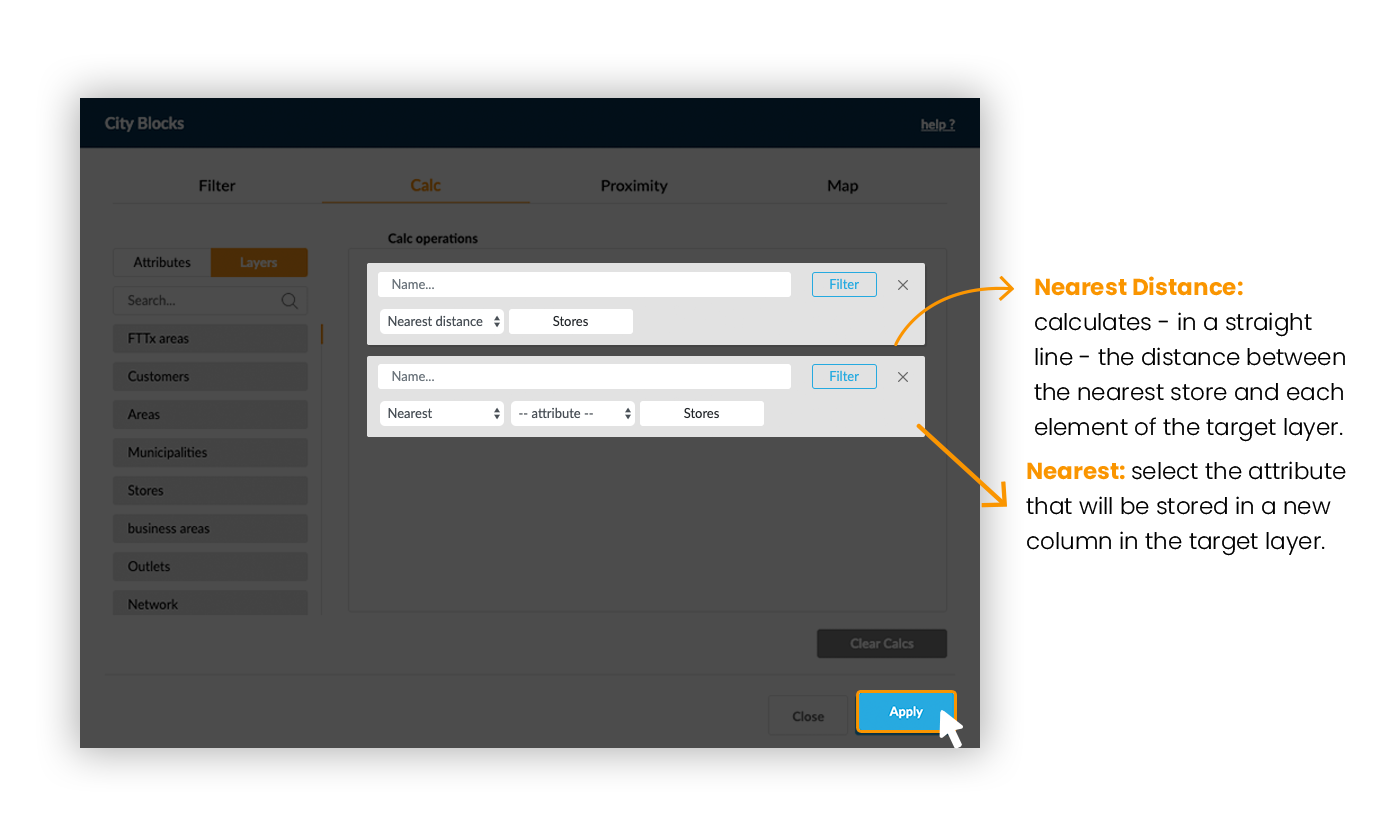
Distance functions (Nearest and Nearest Distance) between 2 point layers are based on straight lines calculations between elements from the two layers.
Exemple: Find the nearest store for each customer and calculate its distance.
When doing a geographic calculation between two polygon layers, one other option will be available: Proportional Sum. It sums the values existing in a polygon taking into account the percentage of overlapped area between two layers.
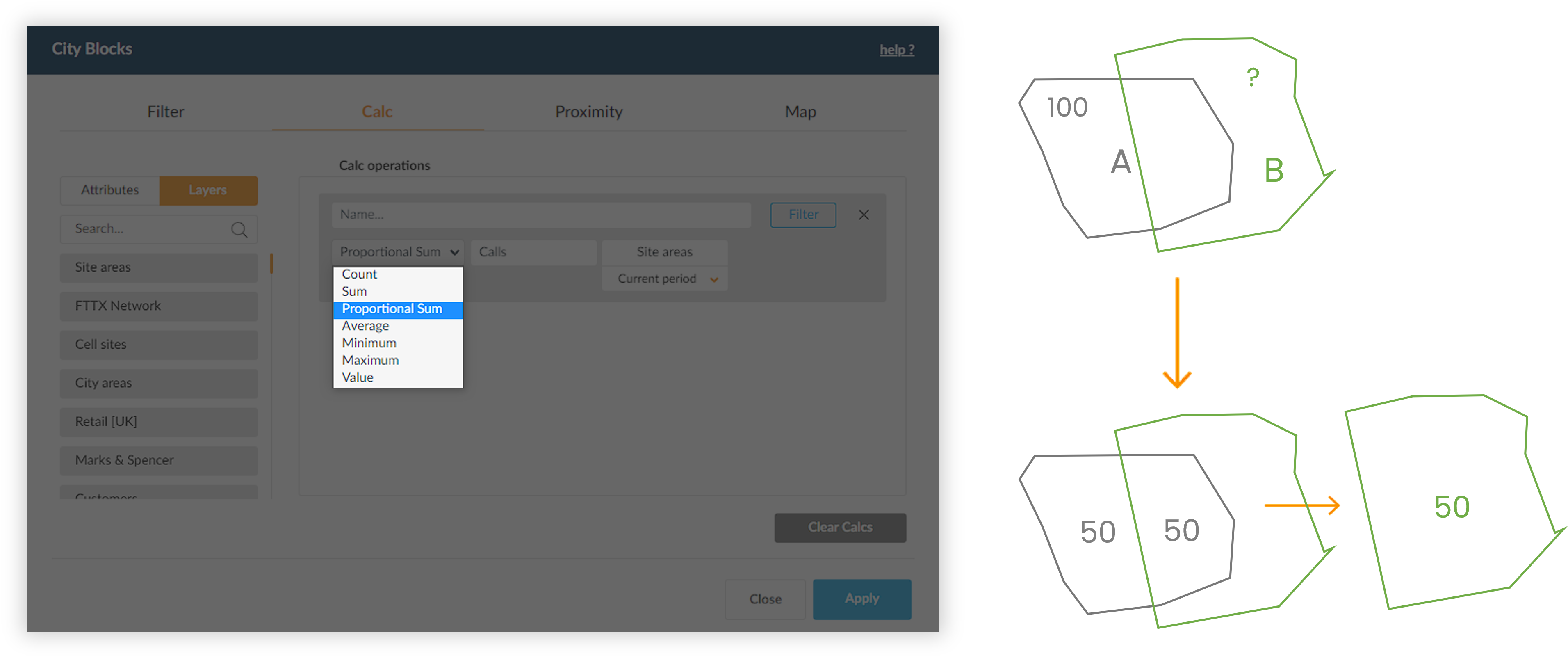
Example: The city area A has 100 residents. If you want to know how many residents live in area B (from a different layer), the Proportional Sum function ponderates the value of the population by the percentage of the area A that overlaps B. In this case, because 50% of A intersects B, the population value will be 100 x 50% = 50 residents.
